Women Reached their “Equal Pay Day” on March 14, Latinas won’t reach theirs until October 5
Equal Pay Day is a powerful reminder of the persistent and unjust gender wage gap that plagues our society and yet, the topic comes up only a few times a year.

Equal Pay Day is a powerful reminder of the persistent and unjust gender wage gap that plagues our society and yet, the topic comes up only a few times a year. Despite incremental progress in recent years, Women’s Equal Pay Day continues to highlight alot of the same old same old.
The day of the equal pay day indicates when the particular group of women “catch up” to white men’s wages from the year before. In 2023, the day all women, including white women, caught up to 2022 wages is March 14. It was March 15th in 2022, and March 24 in 2021.
Not much to write home about in terms of progress.
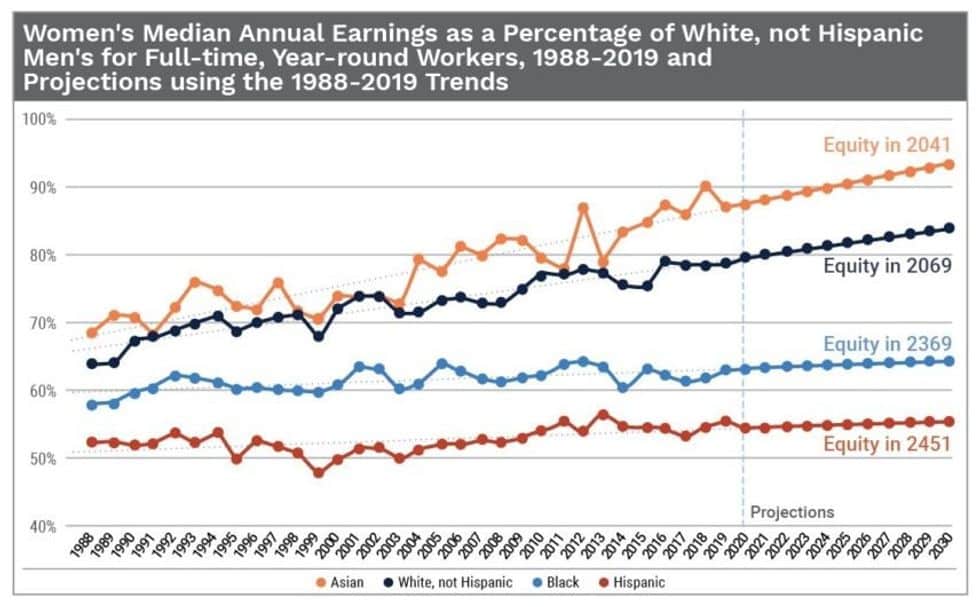
The reality is that the wage gap remains shockingly wide for many women, particularly Latinas. This systemic injustice undermines the value of women’s work and perpetuates gender inequality and economic insecurity. In 2020, Latinas earned just 57 cents to the dollar earned by white men, meaning they would have to work until the age of 90 to earn the same amount that a white man earned by age 60.
The gap worsened to 49 cents in 2021 due to the oversized impact the pandemic had on women in the workforce. It recovered slightly in 2022 to 54 cents, which still meant that Latinas had to work an additional 11 months to earn what a white man earned in a year.
In 2023, the gap saw another slight increase to 57 cents for year-round full-time workers, and the day to raise awareness about the problem lands on October 5, 2023. Latinas consistently remain some of the most underpaid women year after year.
Source: Race and the Pay GapSource: Race and the Pay Gap
According to the Equal Pay Calendar, the data highlights the considerable wage disparities faced by Latinas and women of color, underscoring the disproportionate impact on these groups compared to their white counterparts.
The persistent wage gap for Latinas can be attributed to several factors, including job segregation based on gender and race. Industries that primarily employ women, such as caregiving and domestic work, continue to be undervalued and underpaid, despite being considered essential.
According to the Lean In initiative, this pay disparity extends beyond service-based jobs, with Latinas experiencing minimal support in professional industries. Even with college degrees, Latinas see the worst pay gap compared to white men, and they are less likely to be promoted to management positions.
The pandemic also disproportionately impacted women, particularly in industries where they make up the majority of the workforce. Women were more likely than men to lose their jobs, exacerbating existing inequalities. Women of color face a significant “motherhood penalty,” with many being pushed out of higher-paying jobs for taking time off to give birth. This penalty can have long-term consequences, hindering career advancement for years to come.
These factors all contribute to the persistent wage gap between Latinas and their white male counterparts.
While the Latino community’s significant purchasing power has been a driving force in the economic recovery, it’s alarming that the community’s earning power remains stagnant despite contributing disproportionately to the overall economy. These economic ripple effects have far-reaching consequences and can have a detrimental impact on entire communities and families, acting as a weight that brings them down.
Despite very slow progress, the fight to achieve pay equity continues to build steam year after year. It will take decisive action to close the gender wage gap and ensure that all women are paid fairly for their work.




